Vue3 + TypeScript
使用Vue3+ TypeScript打造一个企业级组件库
1.目录结构§
- 项目结构
- 开发模式讲解
- Vue3的定义
- 单元测试
- 高泛用性的API
- 响应式原理
- 完善功能开发
- 自动化发布流程
2.启动项目准备工作§
1.Vue3更新概览§
- vue RFCS
- slot Api 的变化
- 可通过#header 代表具名插槽
- 全局 Api的变化
- 直接通过import 导入即可
- Compontent-Api
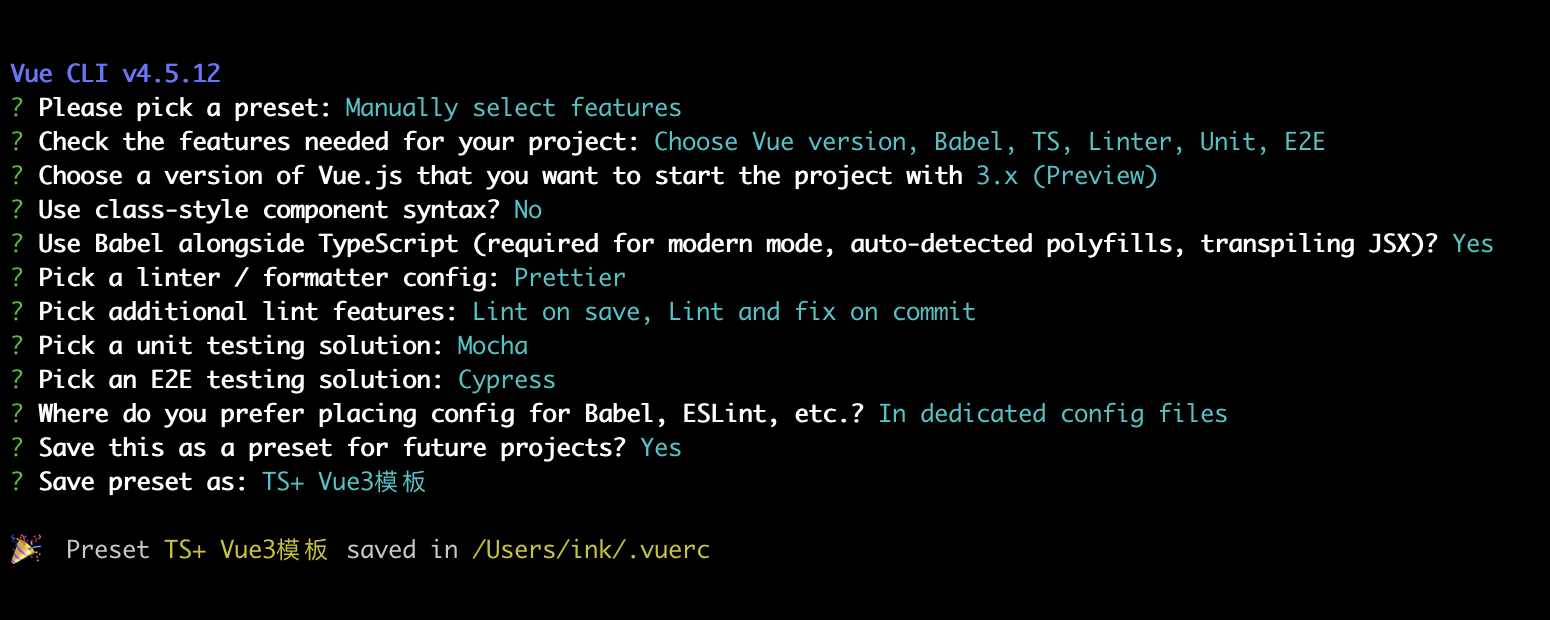
2.使用vue-cli创建TS项目§
- 安装vue-cli
cnpm i -g @vue/cli - 创建项目
vue create project - 配置项目(TS版本)
3.格式化工具prettier§
- 在项目中创建.prettierrc文件
- 配置
{ "semi": false, (不需要分号) "singleQuote": true, (单引号) "arrowParens": "always", (剪头函数需要()) "trailingComma": "all" (结尾以','结束) } - 使用
- 打开设置, 搜索formatter,
- 勾选 Editor: Format On Save 即可(在工作区而不是在user)
4.h函数的详情解读§
- 可使用import的方式导入api
import { createApp, h } from 'vue' createApp(App).mount('#app') - h函数类似react的createElement, 接收三个参数, h(节点类型,节点属性,children选项))
<div id="app"> <img src="/images/h.png" alt=""/> <HelloWorld msg="xasdadas" :age="12" /> </div> 使用h函数可转换成如下代码 const img = require('/images/h.png') // eslint-disable-line const App = defineComponent({ render({ return h('div', { id: 'app' }, [ h('img', { alt: '', src: img }), h(HelloWord, { msg: 'xasdadas', age: 12 }) ]) }) }) - 图片导入这块的可通过require的方式进行导入,如果遇到eslint的报错,可使用// eslint-diasble-line
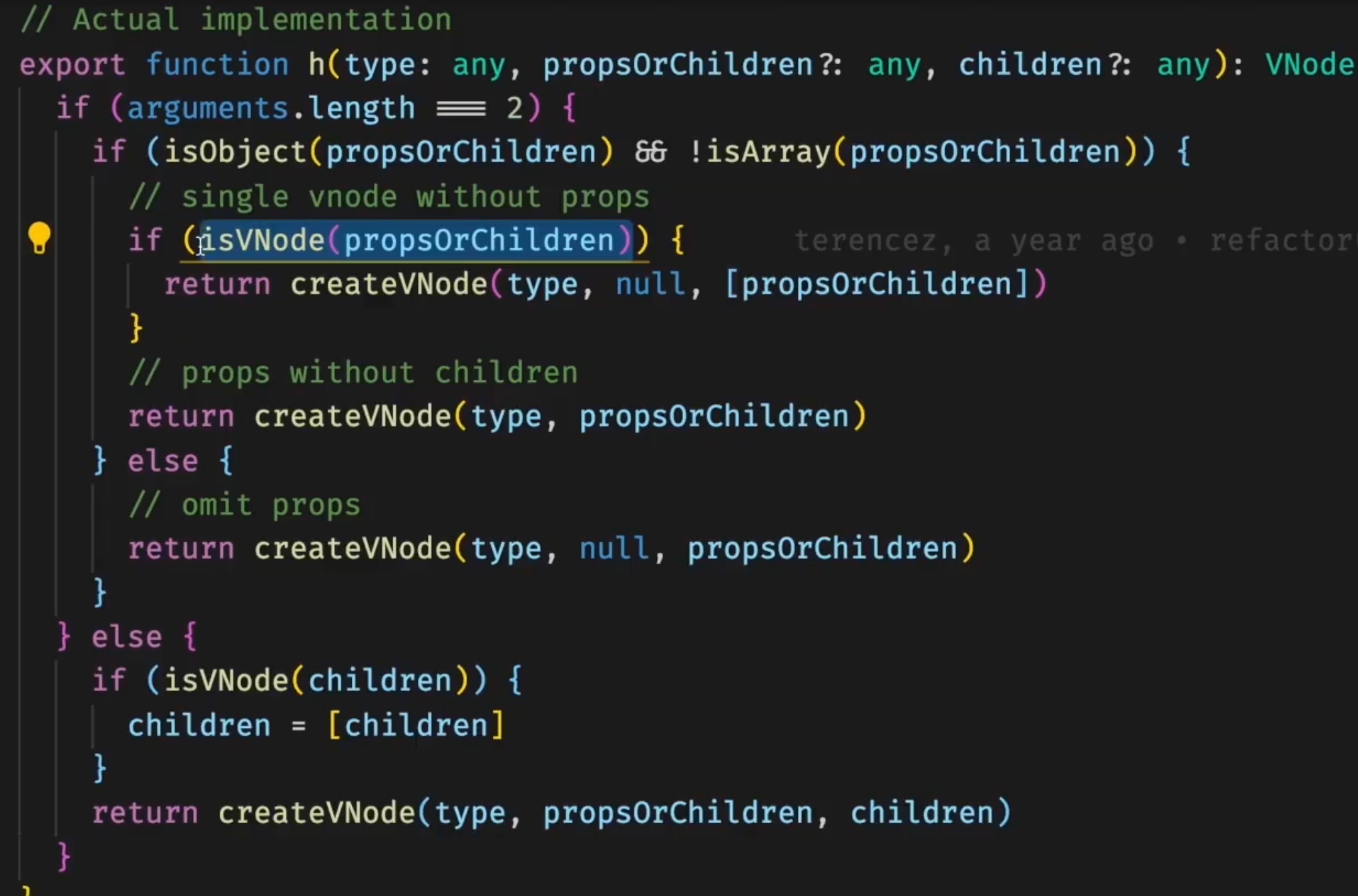
- h函数源码解析
- watchEffect注意点
watchEffect(() => { console.log(h.value) //只监听这个h的值的变化 })
5.使用jsx开发vue3组件§
- 如何改造
- 下载依赖
yarn add @vue/babel-plugin-jsx -D- 在babel.config.js中配置
module.exports = { plugins: ["@vue/babel-plugin-jsx"], }- 创建一个.tsx结尾的文件
import { defineComponent, reactive } from 'vue' import HelloWord from './HelloWorld' function renderHelloWord(num: number) { return <HelloWord age={num} /> } export default defineComponent({ setup() { return () => { const state = reactive({ name: 2, }) return ( <div> {renderHelloWord(9)} <h1>1231</h1> <p>{state.name}</p> </div> ) } }, }) - 使用tsx的优势
- 使用组件时,可提供eslint的格式化校验
- 变量声明
- 抽离共有逻辑,更加灵活
import { defineComponent } from 'vue' const PropsType = { msg: String, age: { type: Number, required: true, }, } as const export default defineComponent({ props: PropsType, setup(props) { return () => ( <div> <span>我是你</span> {props.age} </div> ) }, })
3.Json-schema标准和使用§
1.Ajv校验json-schema§
-
- 下载依赖
yarn add ajv -D -
- 引入ajv
/* eslint-disable */ 在typeScript中使用import会导致报错, 这使用eslint-disable规避require的方式
const Ajv = require('ajv').default
const ajv = new Ajv()
const schema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
name: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 10,
},
age: {
type: 'number',
},
record: {
type: 'array',
items: [{
type: 'string'
},
{
type: 'number'
},
]
}
}
}
const validate = ajv.compile(schema)
const valid = validate({
name: '21312311231asddada',
age: 11,
record: ['sda', 12131]
})
if (!valid) console.log(validate.errors)
- format自定义ajv
const Ajv = require('ajv').default
const ajv = new Ajv()
ajv.addFormat('test', (data) => {
return data === 'hhh'
})
name: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 10,
format: 'tset'
},
2.Ajv自定义关键字§
1. 使用validate
/* eslint-disable */
const Ajv = require('ajv').default
const ajv = new Ajv()
const schema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
name: {
type: 'string',
// minLength: 10,
// format: 'test',
test: false,
},
age: {
type: 'number',
},
record: {
type: 'array',
items: [{
type: 'string'
},
{
type: 'number'
},
]
}
}
}
// 自定义关键字
ajv.addKeyword('test', {
validate(schema, data) {
console.log(schema, data)
if (schema === true) return true
else return data.length === 6
return true
}
})
const validate = ajv.compile(schema)
const valid = validate({
name: 'hhhs22',
age: 11,
record: ['sda', 12131]
})
if (!valid) console.log(validate.errors)
1. 使用compile
ajv.addKeyword('test', {
compile(sche, parentSchema) {
console.log(sche, parentSchema)
return () => true
}
})
需要返回函数
1. 使用mataSchema
ajv.addKeyword('test', {
metaSchema: {
type: 'string'
}
})
会检测每一个校验的值是否为string类型
3.Ajv自定义错误信息§
ajv.addKeyword('test', {
validate: function fun(schema, data) {
fun.errors = [
{
keyword: 'test',
message: '自定义错误信息'
}
]
}
}
4.开发组件库的主流程§
开始实现schema§
一般会创建types文件夹来声明类型§
export enum SchemaTypes {
'NUMBER' = 'number',
'STRING' = 'string',
'INTEGER' = 'interger',
'OBJECT' = 'object',
'ARRAY' = 'array',
'BOOLEAN' = 'boolean',
}
type SchemaRef = { $ref: string }
export interface Schema {
type: SchemaTypes | string
const?: any
format?: string
default?: any
properties?: {
[key: string]: Schema | { $ref: string }
}
item?: Schema | Schema[] | SchemaRef
dependcecies?: {
[key: string]: string[] | Schema | SchemaRef
}
oneOf?: Schema[]
// vjsf?: VueJsonSchemaConfig
required?: string[]
enum?: any[]
enumKeyvalue?: any[]
additionalProperties?: any
additionalItems?: Schema
}
使用vue-jss 可实现css的js化§
import { createUseStyles } from 'vue-jss'
const useStyles = createUseStyles({
container: {
display: 'flex',
flexDirection: 'column',
height: '100%',
width: '1200px',
margin: '0 auto',
}
})
const classesRef = useStyles()
const classes = classesRef.value
<div class={classes.container}>
</div>
- Captain Janeway
Code§
There are many different ways to style code with GitHub's markdown. If you have inline code blocks, wrap them in backticks: var example = true. If you've got a longer block of code, you can indent with four spaces:
if (isAwesome){
return true
}
GitHub also supports something called code fencing, which allows for multiple lines without indentation:
if (isAwesome){
return true
}
And if you'd like to use syntax highlighting, include the language:
if (isAwesome){
return true
}
Highlight specific lines§
site/
|── dist # Output directory
| └── index.html├── pagic.config.ts
└── docs # Source directory └── README.mdTables§
| First Header | Second Header |
|---|---|
| Content from cell 1 | Content from cell 2 |
| Content in the first column | Content in the second column |
Extras§
Pagic supports many extras in markdown.
TeX (KaTeX)§
Inline:
Block: